2023.08.28:原来才刷六十道,假期一百道leetcode宣告失败!
复制带随机指针的链表(中等)
题目描述
给你一个长度为 n
的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random
,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。
深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新
节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的
next 指针和 random
指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点
。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中
X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点
x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y
。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n
个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个
[val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从
0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为
null 。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head
作为传入参数。
思路(两种思路)
思路一:根据next新建节点
遍历原链表,深复制每个节点并附上索引,此处先不管random,再次遍历原链表,获取原链表random节点在原链表的索引,再确定目标链表的对应索引位置
该方法的时间复杂度为o(n^2)
代码一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| class Solution {
public:
int index(Node*root,Node*randomNode){
Node*copy=root;
int indexNum=0;
while(copy){
if(copy==randomNode){
return indexNum;
}
indexNum++;
copy=copy->next;
}
return 0;
}
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
Node* head2=new Node(0);
Node* copy2=head2;
int indecNum;
Node* copy=head;
vector<Node*>sourceNode;
while(copy){
Node* newNode=new Node(copy->val);
head2->next=newNode;
head2=head2->next;
sourceNode.push_back(newNode);
copy=copy->next;
}
head2->next=NULL;
head2=copy2->next;
copy2=head2;
copy=head;
while(head){
if(head->random==NULL){
head2->random=NULL;
}else{
indecNum=index(copy,head->random);
head2->random=sourceNode[indecNum];
}
head=head->next;
head2=head2->next;
}
return copy2;
}
};
|
思路二:根绝random和next新建节点,回溯递归
建立一个哈希表,哈希表存的是原节点和对应节点,如果原节点还没有建立好对应节点,就新建对应节点,然后再新建next和random
代码二
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> cachedNode;
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (!cachedNode.count(head)) {
Node* headNew = new Node(head->val);
cachedNode[head] = headNew;
headNew->next = copyRandomList(head->next);
headNew->random = copyRandomList(head->random);
}
return cachedNode[head];
}
};
|
编辑距离(困难)
题目描述
给你两个单词 word1 和 word2, 请返回将
word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数
。
你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作:
思路
(好难/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~)
动态规划:
dp[i][j]表示word1的前i个要转换为word2的前j个需要的最短步长,比如df[0][0]表示word1的前0个字符转换为word2的前0个字符所需要的步长,就是0,df[2][0]表示word1的前两个字符转换为word2的前两个字符所需的最短步长,即2,就是删除两个字符才能变成长度为0的字符,所以可以对df[0-length1][0]和df[0][0-length2]进行初始化- 然后就是动态方程的设置,
df[i][j]在word1的第i个字符等于word2的第j个字符的时候肯定直接是df[i-1][j-1]+1,不用做什么操作,因为本来就相同了,如果不等就可以考虑题目所说的三种操作:
- 第一种是在让前i-1个字符变成前j-1个字符的前提下进行替换
- 第二种是在让前i-1个字符变成前j个字符的前提下进行删除第i个字符的操作
- 第三种就是在让前i个字符变成前j-1个字符的前提下进行增加第j个字符的操作(注意,这里的i和j针对两个不同的字符串)
- 最后取这三者的最小值
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {
int length1=word1.size();
int length2=word2.size();
vector<vector<int>>df(length1+1,vector<int>(length2+1,0));
for(int i=1;i<=length1;i++){
df[i][0]=i;
}
for(int i=1;i<=length2;i++){
df[0][i]=i;
}
for(int i=0;i<length1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<length2;j++){
if(word1[i]==word2[j])df[i+1][j+1]=df[i][j];
else df[i+1][j+1]=min(df[i][j+1],min(df[i+1][j],df[i][j]))+1;
}
}
return df[length1][length2];
}
};
|
路径总和(中等)
题目描述
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,和一个整数
targetSum ,求该二叉树里节点值之和等于
targetSum 的 路径 的数目。
路径
不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)。
思路
前缀和+哈希(好歹是我自己想出来的/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~)
保存每个节点的前缀和,连续节点的和可以用两个节点的前缀和相减得到结果,为了避免遍历,用哈希保存前缀和结果,用find方便查找答案
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Solution {
public:
int count;
unordered_map<long long,int>path;
void dfsPath(long long allSum,TreeNode*&root,int targetSum){
if(root==NULL){
return;
}
allSum+=root->val;
auto it=path.find(allSum-targetSum);
if(it!=path.end()){
count+=it->second;
}
path[allSum]++;
dfsPath(allSum,root->left,targetSum);
dfsPath(allSum,root->right,targetSum);
path[allSum]--;
}
int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
path[0]=1;
long long allSum=0;
dfsPath(allSum,root,targetSum);
return count;
}
};
|
只出现一次的数字(简单)
题目描述
给你一个 非空 整数数组 nums
,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
你必须设计并实现线性时间复杂度的算法来解决此问题,且该算法只使用常量额外空间。
知识点
异或:
思路(两种思路)
思路一:哈希
时间空间复杂度均为o(n),用哈希存下每个元素出现的次数,超过两次就删除这个元素,最后返回剩下的元素
代码一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int,int>hashMap;
for(int number : nums){
if(++hashMap[number]==2){
hashMap.erase(number);
}
}
return hashMap.begin()->first;
}
};
|
思路二:异或
异或满足交换律,且相同元素异或为0,任意元素异或0为原值
代码二
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
for(int i=1;i<nums.size();i++){
nums[0]^=nums[i];
}
return nums[0];
}
};
|
零钱兑换(中等)
题目描述
给你一个整数数组 coins
,表示不同面额的硬币;以及一个整数 amount
,表示总金额。
计算并返回可以凑成总金额所需的 最少的硬币个数
。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回 -1 。
你可以认为每种硬币的数量是无限的。
思路(两种思路)
思路一:dfs
会超时(刷了快一个月题还是只会暴力求解/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~)
用递归得到能组成余额的最小值
代码一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| class Solution {
public:
int min_size=10000;
void coinMinSize(priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> remainedMoney,int remainedamount,int number){
if(number>=min_size)return;
int money=remainedMoney.top();
int iter=remainedamount/money;
remainedMoney.pop();
if(remainedMoney.empty()){
if(remainedamount%money==0){
min_size=min(min_size,number+iter);
}
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<=iter;i++){
number+=i;
coinMinSize(remainedMoney,remainedamount-i*money,number);
number-=i;
}
}
int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>>remainedMoney;
for(int coin:coins){
remainedMoney.push(coin);
}
coinMinSize(remainedMoney,amount,0);
if(min_size==10000)return -1;
return min_size;
return 1;
}
};
|
思路二:动态规划
dp[i]表示要组成金额为i的硬币需要的最小数量,我们知道硬币一定是从coins里面选一个,因为硬币最后一个肯定也是从coins里面选,那么去掉最后一个的金额需要硬币的数量一定是原本数量-1,因为我们只去掉了最后一个,所以问题就变成了怎么求去掉最后一个的金额的需要的硬币的数量,所以有:
1
| dp[i]=min(dp[i-coin1],dp[i-coin2],dp[i-coin3]……)+1
|
coin代表所拥有的硬币种类,按照该公式对数组进行更新即可
代码二
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| class Solution {
public:
int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {
vector<int>dp(amount+1,10001);
dp[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=amount;i++)
for(int coin:coins)
if(i-coin>=0)dp[i]=min(dp[i-coin]+1,dp[i]);
return dp[amount]==10001?-1:dp[amount];
}
};
|
题目描述
给定 n
个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1
。
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
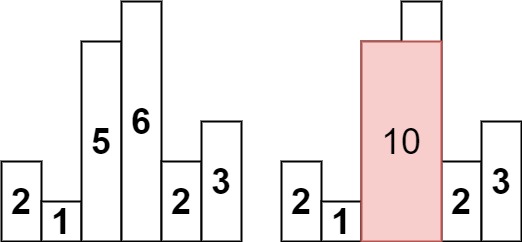
示例 1:
 img
img
1
2
3
| 输入:heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3]
输出:10
解释:最大的矩形为图中红色区域,面积为 10
|
思路(两种思路)
思路一:模仿接雨水的按行求
会超时
(srds这是lz自己的思路,竟然超时了/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~)
求每一行能达到的最大面积,从下往上遍历,获取高度在一定范围的下标
代码一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
vector<int>index1;
int i=*min_element(heights.begin(),heights.end());
int length=heights.size();
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
index1.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>index2;
int use_length=0;
int used_length=0;
int max_area=0;
while(index1.size()!=0){
if(i*index1.size()<=max_area){
break;
}
use_length=0;
for(int j=0;j<index1.size();j++){
used_length=0;
if(j<index1.size()&&heights[index1[j]]>=i){
used_length++;
index2.push_back(index1[j]);
}
while(j<(index1.size()-1)&&(index1[j+1]==index1[j]+1)&&(heights[index1[j+1]]>=i)){
used_length++;
index2.push_back(index1[j]+1);
j++;
}
use_length=max(use_length,used_length);
}
max_area=max(max_area,use_length*i);
i++;
index1=vector<int>(index2.begin(),index2.end());
index2.clear();
}
return max_area;
}
};
|
思路二:运用栈
借鉴了大佬根据栈做的代码
思路有点长直接附上大佬讲解链接:84.
柱状图中最大的矩形 - 力扣(LeetCode)
代码二
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
int length=heights.size();
if(length==0)return 0;
stack<int>index;
int max_area=0;
int top;
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
while(!index.empty()&&heights[i]<heights[index.top()]){
top=index.top();
index.pop();
if(index.empty()){
max_area=max(max_area,(i*heights[top]));
}else{
max_area=max(max_area,(i-index.top()-1)*heights[top]);
}
}
index.push(i);
}
int pre_index;
int now_index=index.top();
int later_index=now_index+1;
while(!index.empty()){
index.pop();
if(index.empty()){
max_area=max(max_area,heights[now_index]*length);
}else{
pre_index=index.top();
max_area=max(max_area,(later_index-pre_index-1)*heights[now_index]);
}
now_index=pre_index;
}
return max_area;
}
};
|
题目描述
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n
个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
思路:双指针
(终于没有超时了啊啊啊!!!!)
设置双指针,题目提示一次遍历,那怎么一次遍历就可以得到倒数节点呢,那就是双指针!,我们知道倒数节点和最后一个节点之间的距离,那最开始就设好两个开始遍历的点,点之间的距离就是倒数的数目,直到靠后的那个节点到达了尾节点,就可以得到我们要删除的节点,一次遍历就可以成功解决
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode*pre=head;
ListNode*later=head;
while(n--){
later=later->next;
}
if(later==NULL)return head->next;
while(later->next!=NULL){
later=later->next;
pre=pre->next;
}
pre->next=pre->next->next;
return head;
}
};
|
搜索二维矩阵(中等)
题目描述
给你一个满足下述两条属性的 m x n 整数矩阵:
- 每行中的整数从左到右按非递减顺序排列。
- 每行的第一个整数大于前一行的最后一个整数。
给你一个整数 target ,如果 target
在矩阵中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
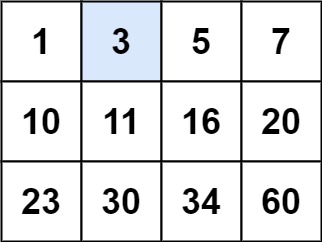
示例 1:
 img
img
1
2
| 输入:matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 3
输出:true
|
思路(两种思路)
思路一:暴力遍历
直接一个元素一个元素比较
代码一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
for(auto its:matrix){
for(int it : its){
if(target==it)return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
|
思路二:两次二分
进行行和列的二分查找
代码二
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>> matrix, int target) {
auto row = upper_bound(matrix.begin(), matrix.end(), target, [](const int b, const vector<int> &a) {
return b < a[0];
});
if (row == matrix.begin()) {
return false;
}
--row;
return binary_search(row->begin(), row->end(), target);
}
};
|
回文链表(简单)
题目描述
给你一个单链表的头节点 head
,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true
;否则,返回 false 。
思路(两种思路)
思路一:借助栈
首先在栈中存一半,另一半进栈是直接对比即可,相同就出栈,不同就说明不是回文链表
代码一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
int length=0;
stack<int>stk;
ListNode*copy=head;
while(copy){
copy=copy->next;
length++;
}
copy=head;
int half_length=length%2;
length/=2;
while(length--){
stk.push(copy->val);
copy=copy->next;
}
if(half_length!=0)copy=copy->next;
int top=0;
while(copy){
top=stk.top();
if(top!=copy->val)return false;
stk.pop();
copy=copy->next;
}
return true;
}
};
|
思路二:反转一半
首先获取链表长度,然后反转后一半,我们可以确定的是对于回文链表另一半反转之后应该和前一半一样(有可能多一个元素,不过前面的值肯定是相同的)
代码二
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* revearse(ListNode*copy){
ListNode *s=NULL;
ListNode *p=copy;
ListNode *q;
while(p){
q=p->next;
p->next=s;
s=p;
p=q;
}
return s;
}
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
int length=0;
ListNode*copy=head;
while(copy){
copy=copy->next;
length++;
}
copy=head;
length/=2;
while(length--){
copy=copy->next;
}
copy=revearse(copy);
while(copy&&head){
if(copy->val!=head->val)return false;
copy=copy->next;
head=head->next;
}
return true;
}
};
|
寻找两个正序数组的中位数(困难)
题目描述
给定两个大小分别为 m 和 n
的正序(从小到大)数组 nums1 和
nums2。请你找出并返回这两个正序数组的
中位数 。
算法的时间复杂度应该为 O(log (m+n)) 。
思路
借鉴了大佬的思路,整体想法是找第k小的位置,比如数组一有n个数,数组二有m个数,如果要找第k小的数,那么这个比k小的数前面就会有k-1个比它小的数,这k-1个数肯定存在于两个数组中,由于两个数组都是增序,如果两个数组比k小的数相等,那么都是k-1/2,如果不相等,肯定有个数组比k小的数小于了k-1/2,这就会导致该数组k-1/2位置的数会比第k小的数字大,同时也可以确认,另一个数组比k小的数大于了k-1/2,那么就会导致k-1/2位置的数肯定会比第k小的数字更小,就可以将该数组的该数字及之前的数字都去掉,那么我们就从找第k个数变成了找第k-((k-1)/2)小的数,因为前面的更小的都被删掉了,最后的终止条件就是找第1小的数字,直接进行比较即可
ps:该方法有很多需要特殊考虑的地方,比如一个数组为空,数组长度不够(k-1)/2等等,需要不断调试,不断运行才能写出正确的代码,lz光提交就提交了十五次/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| class Solution {
public:
double findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
int length1=nums1.size();
int length2=nums2.size();
int status=(length1+length2)%2;
int k=(length1+length2)/2;
if(status)k+=1;
if((length1+length2)==1){
if(length1)return nums1[0];
return nums2[0];
}
int half_k;
while(1){
half_k=k/2;
if(nums1.size()<half_k||(half_k==0&&nums1.size()==0)){
if(nums1.size()>0){
if(nums1[nums1.size()-1]>nums2[half_k-1]){
nums2.assign(nums2.begin()+half_k,nums2.end());
k-=half_k;
}else{
k-=nums1.size();
if(status)return nums2[k-1];
return double(nums2[k-1]+nums2[k])/2;
}
}else{
k-=nums1.size();
if(status)return nums2[k-1];
return double(nums2[k-1]+nums2[k])/2;
}
}else if(nums2.size()<half_k||(half_k==0&&nums2.size()==0)){
if(nums2.size()>0){
if(nums2[nums2.size()-1]>nums1[half_k-1]){
nums1.assign(nums1.begin()+half_k,nums1.end());
k-=half_k;
}else{
k-=nums2.size();
if(status)return nums1[k-1];
return double(nums1[k-1]+nums1[k])/2;
}
}else{
k-=nums2.size();
if(status)return nums1[k-1];
return double(nums1[k-1]+nums1[k])/2;
}
}else if(half_k!=0){
if(nums1[half_k-1]<nums2[half_k-1]){
nums1.assign(nums1.begin()+half_k,nums1.end());
}else{
nums2.assign(nums2.begin()+half_k,nums2.end());
}
k-=half_k;
}
if(k==1){
if(nums1.size()==0){
if(status)return nums2[0];
return double(nums2[0]+nums2[1])/2;
}
if(nums2.size()==0){
if(status)return nums1[0];
return double(nums1[0]+nums1[1])/2;
}
if(status)return min(nums1[0],nums2[0]);
if(nums1[0]==nums2[0])return double(nums1[0]);
if(nums1[0]<nums2[0]&&nums1.size()>=2)return double(nums1[0]+min(nums1[1],nums2[0]))/2;
if(nums2[0]<nums1[0]&&nums2.size()>=2)return double(nums2[0]+min(nums2[1],nums1[0]))/2;
return double(nums1[0]+nums2[0])/2;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
|
寻找重复数(中等)(待做)
题目描述
给定一个包含 n + 1 个整数的数组 nums
,其数字都在 [1, n] 范围内(包括 1 和
n),可知至少存在一个重复的整数。
假设 nums 只有 一个重复的整数 ,返回
这个重复的数 。
你设计的解决方案必须 不修改 数组 nums
且只用常量级 O(1) 的额外空间。
思路
颜色分类(中等)
题目描述
给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色、共 n 个元素的数组
nums ,原地对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
我们使用整数 0、 1 和 2
分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
必须在不使用库内置的 sort 函数的情况下解决这个问题。
思路
看起来代码比较复杂但是只遍历了一次数组,不知道能不能缩减,希望大佬能帮我看看,总体思路是:
由于题目确定了只有三个数字,所以我选择用双指针i和j,从头和尾往中间走,im表示im之前已经排好0的位置,jm表示jm之后已经排好2的位置,如果i和j遇到了0或者2,就放到im后一个位置或者jm前一个位置,知道遍历到i==j就说明遍历完了
就相当于把0往前扔,把2往后扔,1不变
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| class Solution {
public:
void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {
int length=nums.size();
int i,j;
int im=-1;
int jm=length;
while(im<length-1&&nums[im+1]==0)im++;
i=im+1;
while(i<length&&nums[i]==1)i++;
while(jm>=1&&nums[jm-1]==2)jm--;
j=jm-1;
while(j>=0&&nums[j]==1)j--;
while(i<length&&j>=0&&i<=j){
if(nums[i]==2&&nums[j]==0){
if(j==jm-1&&i!=im+1){
swap(nums[j--],nums[++im]);
swap(nums[i++],nums[--jm]);
}else if(j==jm-1&&i==im+1){
swap(nums[j--],nums[i++]);
++im;
--jm;
}else{
swap(nums[i++],nums[--jm]);
swap(nums[j--],nums[++im]);
}
}else if(nums[i]==0&&nums[j]==0){
swap(nums[i++],nums[++im]);
swap(nums[++im],nums[j--]);
if(im==i)i++;
}else if(nums[i]==0&&nums[j]==2){
swap(nums[i++],nums[++im]);
swap(nums[j--],nums[--jm]);
}else if(nums[i]==2&&nums[j]==2){
swap(nums[i++],nums[--jm]);
swap(nums[j--],nums[--jm]);
if(j==jm)j--;
}
while(im<length-1&&nums[im+1]==0)im++;
i=im+1;
while(i<length&&nums[i]==1)i++;
while(jm>=1&&nums[jm-1]==2)jm--;
j=jm-1;
while(j>=0&&nums[j]==1)j--;
}
}
};
|
二叉树的中序遍历(简单)
题目描述
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的
中序 遍历 。
思路
规规矩矩中序遍历即可,很简单
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| class Solution {
public:
vector<int>ans;
void mid(TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL)return;
mid(root->left);
ans.push_back(root->val);
mid(root->right);
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
mid(root);
return ans;
}
};
|
搜索旋转排序数组(中等)
题目描述
整数数组 nums 按升序排列,数组中的值
互不相同 。
在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标
k(0 <= k < nums.length)上进行了
旋转,使数组变为
[nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]](下标
从 0 开始 计数)。例如, [0,1,2,4,5,6,7]
在下标 3 处经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]
。
给你 旋转后 的数组 nums 和一个整数
target ,如果 nums 中存在这个目标值
target ,则返回它的下标,否则返回 -1 。
你必须设计一个时间复杂度为 O(log n)
的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
1
2
| 输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
输出:4
|
知识点
c++合并数组(vector)
1
2
3
4
5
6
| vector<int> vec1 = {...};
vector<int> vec2 = {...};
vector<int> vec3;
vec3.insert(vec3.end(),vec1.begin(),vec1.end())
vec3.insert(vec3.end(),vec2.begin(),vec2.end())
|
思路
由题得,如果数组预先进行了旋转,那么数组可以分为升序的两部分,可以用二分法找到第二个升序的起始点,也就是找到第一个小于nums[0]的点,然后确定target属于哪个区间,在区间再进行二分查找即可
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left=0;
int right=nums.size()-1;
int mid;
if(nums[right]<nums[left]){
while(left<right-1){
mid=(left+right)/2;
if(nums[mid]>=nums[left])left=mid;
else right=mid;
}
if(nums[right]>target)return -1;
if(nums[0]>target){
left=right;
right=nums.size()-1;
}else{
left=0;
right=right-1;
}
}
while(left<right-1){
mid=(left+right)/2;
if(nums[mid]<=target)left=mid;
else right=mid;
}
if(nums[left]!=target&&nums[right]!=target)return -1;
return nums[left]==target?left:right;
}
};
|
合并区间(中等)
题目描述
以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为
intervals[i] = [starti, endi]
。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回
一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间 。
知识点
优先队列+pair小根堆
1
| priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,greater<pair<int,int>>>pq;
|
思路
使用优先队列+pair自动排序,然后一个一个取出来比较就可以了(但是好像直接sort就行)
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>>& intervals) {
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,greater<pair<int,int>>>nums;
for(auto it : intervals){
nums.emplace(it[0],it[1]);
}
vector<vector<int>>ans;
int first,second;
first=nums.top().first;
second=nums.top().second;
nums.pop();
while(!nums.empty()){
if(nums.top().first>second){
ans.push_back({first,second});
first=nums.top().first;
second=nums.top().second;
}else{
second=max(second,nums.top().second);
}
nums.pop();
}
ans.push_back({first,second});
return ans;
}
};
|
岛屿数量(中等)
题目描述
给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和
'0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
示例 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| 输入:grid = [
["1","1","1","1","0"],
["1","1","0","1","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","0","0","0"]
]
输出:1
|
示例 2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| 输入:grid = [
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","1","0","0"],
["0","0","0","1","1"]
]
输出:3
|
思路
二维数组的dfs遍历
和二叉树相似,二叉树前序遍历思路是先遍历左节点,再遍历右节点,二维矩阵的遍历是先遍历左边,然后上面,右面,下面,这样遍历的结果肯定是属于一个岛的,遍历四个方向即可,同时由于不同点可能会遍历到同一个地方,将遍历过的地方进行标记,以免重复,此题的思路就是先遍历到第一个等于1的点,然后从四个方向进行遍历,将遍历的点都标记为2,这样下次遍历就不会再遍历到该点,有点像消消乐,从一个点往周围延申,全部遍历到并消除
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>&grid,int i,int j){
if(i>=grid.size()||j>=grid[0].size()||i<0||j<0||grid[i][j]!='1')return;
grid[i][j]='2';
dfs(grid,i-1,j);
dfs(grid,i+1,j);
dfs(grid,i,j+1);
dfs(grid,i,j-1);
}
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int gridnum=0;
for(int i=0;i<grid.size();i++){
for(int j=0;j<grid[0].size();j++){
if(grid[i][j]=='1'){
gridnum++;
dfs(grid,i,j);
}
}
}
return gridnum;
}
};
|
二叉树的层序遍历(中等)
题目描述
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的
层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
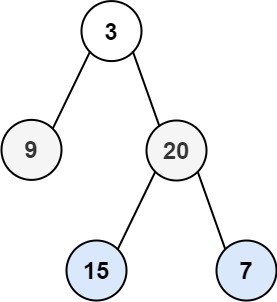
示例 1:
 img
img
1
2
| 输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
|
知识点
c++ vector基本用法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| queue 和 stack 有一些成员函数相似,但在一些情况下,工作方式有些不同:
front():返回 queue 中第一个元素的引用。如果 queue 是常量,就返回一个常引用;如果 queue 为空,返回值是未定义的。
back():返回 queue 中最后一个元素的引用。如果 queue 是常量,就返回一个常引用;如果 queue 为空,返回值是未定义的。
push(const T& obj):在 queue 的尾部添加一个元素的副本。这是通过调用底层容器的成员函数 push_back() 来完成的。
push(T&& obj):以移动的方式在 queue 的尾部添加元素。这是通过调用底层容器的具有右值引用参数的成员函数 push_back() 来完成的。
pop():删除 queue 中的第一个元素。
size():返回 queue 中元素的个数。
empty():如果 queue 中没有元素的话,返回 true。
emplace():用传给 emplace() 的参数调用 T 的构造函数,在 queue 的尾部生成对象。
swap(queue<T> &other_q):将当前 queue 中的元素和参数 queue 中的元素交换。它们需要包含相同类型的元素。也可以调用全局函数模板 swap() 来完成同样的操作。
|
思路
比较简单,用队列,先进后出原则,先将root存进队列,这个时候相当于第一层,所以只遍历root一个点即可,先获取当前队列长度为1,即当前遍历次数,然后存进left和right,再将root给pop掉,接着继续遍历第二层,也就是上一层存进的left和right,直接获取队列长度作为遍历次数即可
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*>node;
vector<vector<int>>ans;
vector<int>tempans;
node.push(root);
int length;
while(!node.empty()){
length=node.size();
while(length--){
if(node.front()){
tempans.push_back(node.front()->val);
node.push(node.front()->left);
node.push(node.front()->right);
}
node.pop();
}
if(!tempans.empty())ans.push_back(tempans);
tempans.clear();
}
return ans;
}
};
|
对称二叉树(简单)
题目描述
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
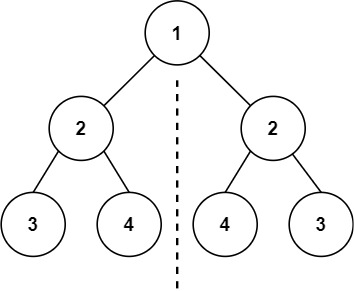
示例 1:
 img
img
1
2
| 输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
|
思路
用递归遍历即可,很好发现对称二叉树的规律,首先分为两部分,root的左节点和右节点,比较两节点值是否相等,相等就在比较root左节点的右节点和root右节点的左节点值是否相等
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| class Solution {
public:
bool compare(TreeNode*Node1,TreeNode*Node2){
if(Node1==NULL&&Node2==NULL)return true;
if(Node1==NULL||Node2==NULL||Node1->val!=Node2->val)return false;
return compare(Node1->left,Node2->right)&&compare(Node1->right,Node2->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
return compare(root->left,root->right);
}
};
|
最小路径和(中等)
题目描述
给定一个包含非负整数的 *m* x *n* 网格 grid
,请找出一条从左上角到右下角的路径,使得路径上的数字总和为最小。
说明:每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。
示例 1:
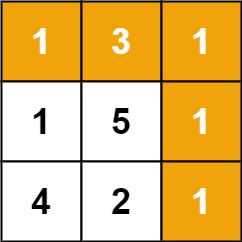 img
img
1
2
3
| 输入:grid = [[1,3,1],[1,5,1],[4,2,1]]
输出:7
解释:因为路径 1→3→1→1→1 的总和最小。
|
思路
这个题感觉做过啊,但是leetcode没显示,那就再做一遍吧OvO
dp[i][j]代表的是到达(i,j)位置的最短路径,等于到达(i-1,j)的最短路径和到达(i,j-1)的最短路径的较小值+grid[i][j]
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| class Solution {
public:
int minPathSum(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
vector<vector<int>>dp(grid.size()+1,vector<int>(grid[0].size()+1,0));
for(int i=1;i<=grid.size();i++)
dp[i][1]=dp[i-1][1]+grid[i-1][0];
for(int j=1;j<=grid[0].size();j++)
dp[1][j]=dp[1][j-1]+grid[0][j-1];
for(int i=2;i<=grid.size();i++)
for(int j=2;j<=grid[0].size();j++)
dp[i][j]=min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1])+grid[i-1][j-1];
return dp[grid.size()][grid[0].size()];
}
};
|
合并K个升序链表(困难)
题目描述
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| 输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
|
思路
合并k个有序链表也许很陌生,但是合并两个有序链表就好做很多,比如第一个示例,可以看作先合并前两个,再和最后一个合并,和二分法的思维很类似,比如现在有长度为7的lists,第一轮合并lists[0]+lists[1],
lists[2]+lists[3],
lists[4]+lists[5],最后添上list[6],得到长度为4的新链表组,继续两两合并直到最后新链表组长度为1即可
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* merge2Lists(ListNode* list1,ListNode* list2){
ListNode*ans=new ListNode();
ListNode*tempans=ans;
while(list1&&list2){
while(list2&&list1&&list1->val<=list2->val){
tempans->next=list1;
tempans=tempans->next;
list1=list1->next;
}
while(list1&&list2&&list2->val<list1->val){
tempans->next=list2;
tempans=tempans->next;
list2=list2->next;
}
}
if(list1){
tempans->next=list1;
}else if(list2){
tempans->next=list2;
}
return ans->next;
}
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
if(lists.size()==0||(lists.size()==1&&lists[0]==NULL))return NULL;
vector<ListNode*>templists;
while(lists.size()!=1){
for(int i=0;i<lists.size()/2;i++){
templists.push_back(merge2Lists(lists[i*2],lists[i*2+1]));
}
if(lists.size()%2)templists.push_back(lists.back());
lists.assign(templists.begin(),templists.end());
templists.clear();
}
return lists[0];
}
};
|









